Definition
Overpronation, or flat feet, is a common biomechanical problem that occurs in the walking process when a person’s arch collapses upon weight bearing. This motion can cause extreme stress or inflammation on the plantar fascia, potentially causing discomfort and leading to other foot problems.
Cause
Overpronation is very prominent in people who have flexible, flat feet. The framework of the foot begins to collapse, causing the foot to flatten and adding stress to other parts of the foot. As a result, overpronation can lead to Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Metatarsalgia, Post-tib Tendonitis and/or Bunions.
There are many causes of flat feet. Obesity, pregnancy, or repetitive pounding on a hard surface can weaken the arch leading to overpronation. Often people with flat feet do not experience discomfort immediately, and some never suffer from any discomfort at all. However, when symptoms develop and become painful, walking becomes awkward and can cause increased strain on the feet or calves.
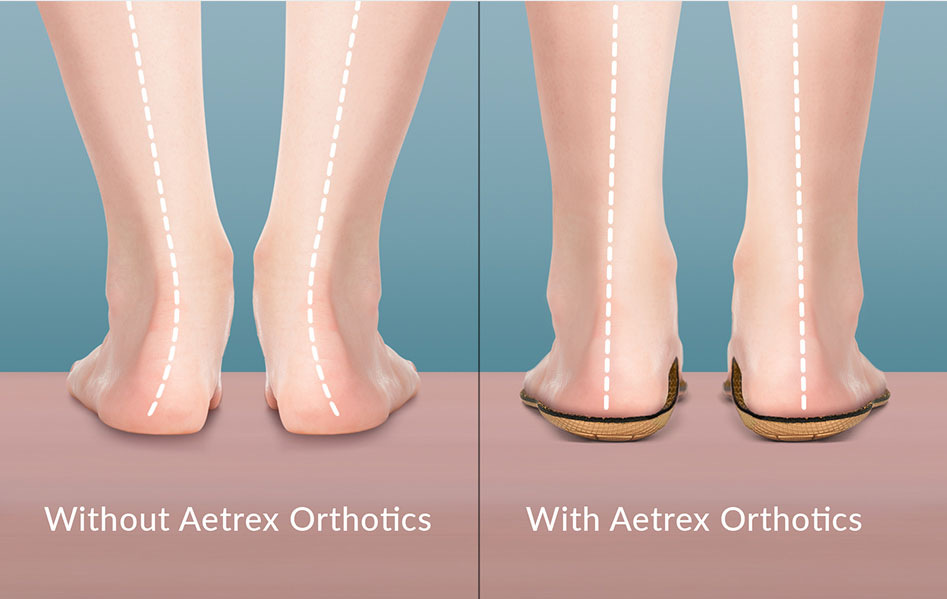
Treatment and Prevention
Overpronation can be treated conservatively with orthotics designed with proper arch support and medial rearfoot posting to help prevent the overpronation. Footwear should also be examined to ensure a proper fit. Footwear with firm heel counters are often recommended for extra support and stability. Improperly fitting footwear can also lead to additional foot problems.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Share:
Diabetes