
Achilles Tendonitis
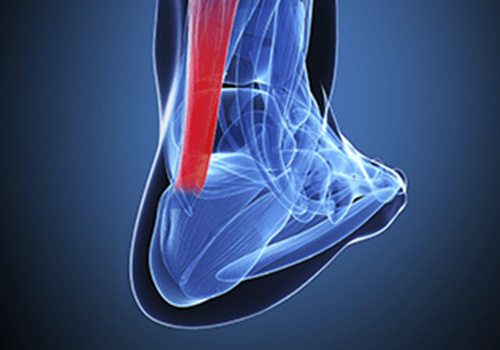
Definition
Achilles tendonitis is inflammation of the Achilles tendon and can lead to degeneration. The achilles tendon is the large tendon located in the back of the leg that inserts into the heel. The pain caused by achilles tendonitis can develop gradually without a history of trauma. The pain can be a shooting pain, burning pain, or even an extremely piercing pain. Achilles tendonitis should not be left untreated due to the danger that the tendon can become weak and ruptured.
Cause
There are several factors that can cause Achilles Tendonitis. The most common cause is over-pronation. Over-pronation occurs in the walking and/or running process when the arch collapses upon weight-bearing, adding stress on the Achilles tendon. Other factors that lead to Achilles Tendonitis are improper shoe selection, inadequate stretching prior to engaging in athletics, a short Achilles tendon, direct trauma (injury) to the tendon, and heel bone deformity.
Treatment and Prevention
Athletes, particularly runners, should incorporate a thorough stretching program to properly warm-up the muscles. They should decrease the distance of their walk or run, apply ice after the activity and avoid any uphill climbs. Those with Achilles tendonitis should wear lightweight, shock-absorbing orthotics to help reduce stress and pressure on the Achilles tendon. The orthotic can help control over-pronation, support the longitudinal arch, and reduce stress on the Achilles tendon. If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Arch Pain
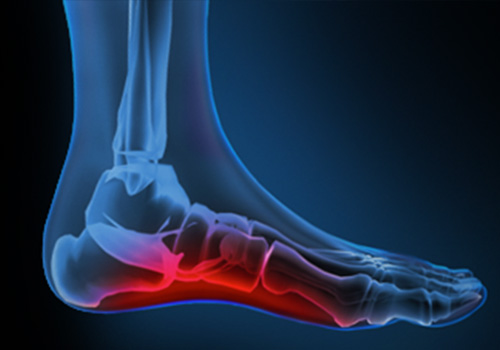
Definition
The term arch pain (often referred to as arch strain) refers to inflammation and/or a burning sensation at the arch of the foot.
Cause
There are many different factors that can cause arch pain. A structural imbalance or an injury to the foot can often be the direct cause. However, most frequently the cause is a common condition called Plantar Fasciitis. The plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue located along the bottom surface of the foot that runs from the heel to the forefoot. Excessive stretching of the plantar fascia, usually due to over-pronation (flat feet), causes plantar fasciitis. The inflammation caused by the plantar fascia being stretched away from the calcaneus (heel bone) often leads to pain in the heel and arch areas. The pain is often extreme in the morning when an individual first gets out of bed or after a prolonged period of rest. If this condition is left untreated and strain on the longitudinal arch continues, a bony protrusion may develop, known as a heel spur. It is important to treat the condition promptly before it worsens.
Treatment and Prevention
This is a common foot condition that often can be easily treated. If you suffer from arch pain avoid high-heeled shoes whenever possible. Try to choose footwear with a reasonable heel, soft uppers, shock-absorbing soles, and proper arch support. When the arch pain is pronation-related (flat feet), an orthotic designed with a medial heel post and proper arch support is recommended for treating the condition. This type of orthotic will help control over-pronation, support the arch, and provide the necessary relief.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Bunions
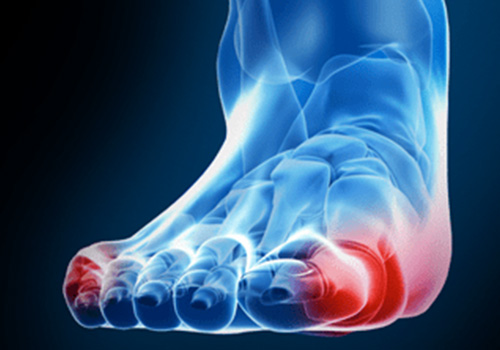
Definition
Bunions, referred to in the medical community as Hallux Valgus, are one of the most common forefoot problems. A bunion is a prominent bump on the inside of the foot around the big toe joint. This bump is actually a bone protruding towards the inside of the foot. With the continued movement of the big toe toward the smaller toes, it is common to find the big toe resting under or over the second toe. This can cause a common forefoot condition called overlapping toes. Some of the symptoms of bunions include inflammation, swelling, and soreness on the side surface of the big toe. The discomfort commonly causes a patient to walk improperly. Another type of bunion which some individuals experience is called a Tailor’s Bunion, also known as a Bunionette. This forms on the outside of the foot toward the joint at the 5th toe. It is a smaller bump that forms due to the 5th toe moving inward, toward the big toe.
Cause
Bunions are a common problem experienced mostly by women. The deformity can develop from an abnormality in foot function or from arthritis, but is more commonly caused by wearing improper fitting footwear. Tight, narrow dress shoes with a constrictive toe box (toe area) can cause the foot to begin to take the shape of the shoe, leading to the formation of a bunion. Women who have bunions normally wear dress shoes that are shaped improperly for their feet. Their toes are squeezed together in their shoes causing the first metatarsal bone to protrude on the side of the foot.
Treatment and Prevention
Conservative treatment to alleviate the pain associated with bunions is to wear shoes that accommodate the deformity. Shoes designed with a wide toe box are recommended. Orthotics are also recommended for this condition to support the arch in the case of flat feet. Orthotics can limit the progression of the bunion formation and help provide relief.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Heel Pain
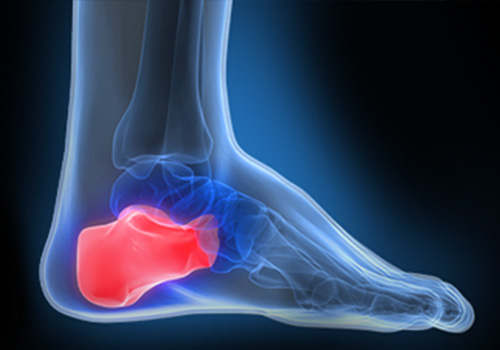
Definition
Heel pain is a common condition in which weight bearing on the heel causes extreme discomfort.
Cause
There are two different categories of heel pain. The first is caused by overuse repetitive stress which refers to a soreness resulting from too much impact on a specific area of the foot. This condition, often referred to as “heel pain syndrome,” can be caused by shoes with heels that are too low, a thinned out fat pad in the heel area, or from a sudden increase in activity. Plantar Fasciitis, the other very common diagnosis of heel pain, is usually caused from a biomechanical problem, such as over-pronation (flat feet). The plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue that runs along the bottom surface of the foot, from the calcaneus (heel bone) through the midfoot and into the forefoot. Over-pronation can cause the plantar fascia to be excessively stretched and inflamed, resulting in pain in the heel and arch areas of the foot. Often the pain will be most intense first thing in the morning or after a prolonged period of rest. The pain often gradually subsides as the day progresses.
Treatment and Prevention
To properly treat heel pain, you must absorb shock, provide cushioning and elevate the heel to transfer pressure. This can be accomplished with an orthotic designed with materials that will absorb shock and provide cushioning. When the condition is pronation related (usually plantar fasciitis), an orthotic with medial posting and good arch support will help control the pronation and prevent the inflammation of the plantar fascia. Footwear selection is also an important criteria when treating heel pain. Shoes with a firm heel counter, good arch support, and appropriate heel height are often recommended.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Heel Spurs
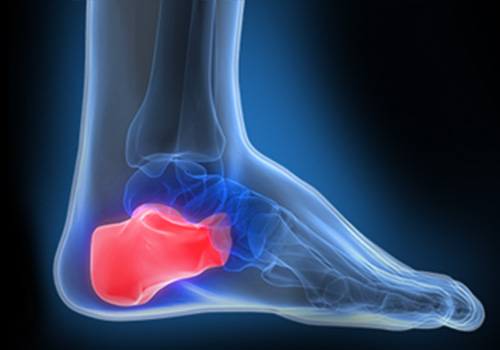
Definition
The calcaneus (heel bone) is the largest bone in the foot and absorbs the most amount of shock and pressure. A heel spur develops as an abnormal growth of the heel bone. Calcium deposits form when the plantar fascia pulls away from the heel area, causing a bony protrusion, or heel spur. The plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue located along the bottom surface of the foot that runs from the heel to the forefoot. Heel spurs can cause extreme pain in the rearfoot, especially while standing or walking.
Cause
Heel spurs develop as an abnormal growth in the heel bone due to calcium deposits that form when the plantar fascia pulls away from the heel. This stretching of the plantar fascia is usually the result of over-pronation (flat feet), but people with very high arches can also develop heel spurs. Women have a significantly higher incidence of heel spurs due to the types of footwear often worn on a regular basis.
Treatment and Prevention
The key for the proper treatment of heel spurs is determining what is causing the excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. When the cause is over-pronation (flat feet), an orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support is an effective device to reduce the over-pronation, and allow the condition to heal. Other common treatments include stretching exercises, losing weight and wearing shoes that have a cushioned heel that absorbs shock. Orthotics can provide extra comfort, cushion to the heel, and reduce the amount of shock and shear forces experienced from everyday activities.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Metatarsalgia
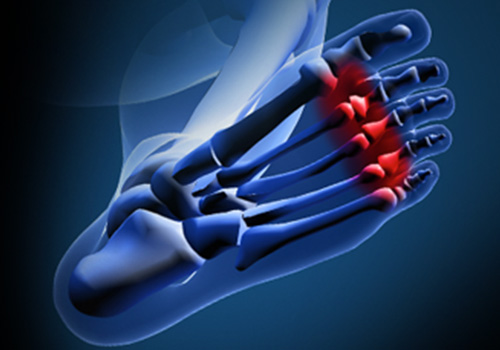
Definition
Metatarsalgia is a general term used to denote a pain in the metatarsal region of the foot (the area just before the toes, more commonly referred to as the ball-of-the-foot). This is a common foot problem that can affect the bones and joints at the ball-of-the-foot. Metatarsalgia (ball-of-foot-pain) is often located under the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th metatarsal heads, or more isolated at the first metatarsal head (near the big toe).
Cause
With this common foot condition, one or more of the metatarsal heads become painful and/or inflamed, usually due to excessive pressure over a long period of time. Ball-of-foot pain is often caused from improper fitting footwear, most frequently by women’s dress shoes and other restrictive footwear. Footwear with a narrow toe box (toe area) forces the ball-of-foot area to be forced into a minimal amount of space. This can inhibit the walking process and lead to extreme discomfort in the forefoot. Other factors can cause excessive pressure in the ball-of-foot area that can result in metatarsalgia. These include shoes with heels that are too high or participating in high impact activities without proper footwear and/or orthotics. Also as we get older, the fat pad in our foot tends to thin out, making us much more susceptible to pain in the ball-of-the-foot.
Treatment and Prevention
The first step in treating metatarsalgia is to determine the cause of the pain. If improper fitting footwear is the cause of the pain, the footwear must be changed. Footwear designed with a high, wide toe box (toe area) and shock absorbing soles are recommended for metatarsalgia.
Unloading pressure to the ball-of-the-foot can be accomplished with a variety of footcare products. Orthotics designed to relieve ball-of-foot pain usually feature a metatarsal pad. The orthotic is constructed with the pad placed behind the ball-of-the-foot to relieve pressure and redistribute weight from the painful area to more tolerant areas. When they are used with proper footwear, you should experience significant relief.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Morton's Neuroma
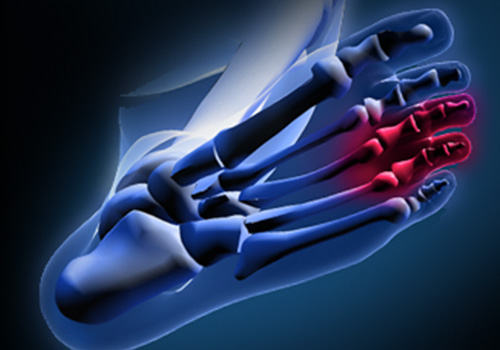
Definition
Morton’s Neuroma is a common foot problem associated with pain, swelling and/or an inflammation of a nerve, usually at the ball-of-the-foot between the 3rd and 4th toes. Symptoms of this condition include sharp pain, burning, and possibly even a lack of feeling in the affected area. Morton’s Neuroma may also cause numbness, tingling, or cramping in the forefoot.
Cause
Morton’s Neuroma is a foot condition caused from an abnormal function of the foot that leads to bones squeezing a nerve, usually between the 3rd and 4th metatarsal heads. Symptoms of Morton’s Neuroma often occur during or after you have been placing significant pressure on the forefoot area, possibly by walking, standing, jumping, or sprinting. This condition can also be caused by footwear selection. Footwear with pointed toes and/or high heels can often lead to the neuroma. Constricting shoes can pinch the nerve between the toes, leading to discomfort and extreme pain.
Treatment and Prevention
The first step in treating Morton’s Neuroma is to select proper footwear. Footwear with a high and wide toe box (toe area) is ideal for treating and relieving the pain. The next step in treatment is to use an orthotic designed with a metatarsal pad. This pad is located behind the ball-of-the-foot to unload pressure, and relieve the pain caused by the neuroma.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Plantar Fasciitis
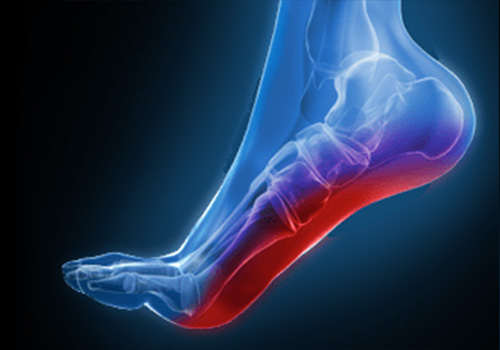
Definition
Plantar Fasciitis is an inflammation caused by excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue which runs along the bottom surface of the foot, attaching at the bottom of the calcaneus (heel bone) and extending to the forefoot. When the plantar fascia is excessively stretched, this can cause plantar fasciitis, which can also lead to heel pain, arch pain, and even heel spurs.
Cause
The excessive stretching of the plantar fascia that leads to the inflammation and discomfort is most commonly caused by over-pronation (flat feet). Over-pronation occurs in the walking process, when a person’s arch collapses upon weight bearing, causing the plantar fascia to be stretched away from the calcaneus (heel bone). Other causes can include: a foot with an unusually high arch, a sudden increase in physical activity, excessive weight on the foot, usually attributed to obesity or pregnancy, or even improperly fitting footwear.
With Plantar Fasciitis, the bottom of your foot usually hurts near the inside of the foot where the heel and arch meet. The pain is often acute either first thing in the morning or after a long rest, because while resting the plantar fascia contracts back to its original shape. As the day progresses and the plantar fascia continues to be stretched, the pain can subside gradually.
Treatment and Prevention
The key for the proper treatment of Plantar Fasciitis is determining what is causing the excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. When the cause is over-pronation (flat feet), an orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support is an effective device to reduce the over-pronation and allow the condition to heal. If you have very high arches, which can also lead to plantar fasciitis, cushioning the heel, absorbing shock and wearing proper footwear will increase comfort of the foot. Other common treatments include stretching exercises, wearing orthotic sandals or wearing shoes that have arch support and cushioned heels to absorb shock.
Every time your foot strikes the ground, the plantar fascia is stretched. You can reduce the strain and stress on the plantar fascia by avoiding running on hard or uneven ground, losing any excess weight, and wearing shoes and orthotics that support your arch to prevent overstretching of the plantar fascia.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Pregnancy and Your Feet
Definition
Pregnancy triggers many different changes in a woman’s body. Due to the natural weight gain during pregnancy, a woman’s center of gravity is completely altered. This causes a new weight-bearing stance and added pressure to the knees and feet. Two of the most common foot problems experienced by pregnant woman are over-pronation and edema. These problems can lead to pain at the heel, arch, or the ball-of-foot. Because of this, it is important for all pregnant women to learn more about foot health during their pregnancy to help make this nine month period more comfortable.
Treatment and Prevention
There are effective ways to treat both over-pronation and edema during pregnancy. Over-Pronation can be treated conservatively with orthotics designed with appropriate arch support and medial rearfoot posting to correct the over-pronation. Comfortable, supportive footwear is also very important in treating over-pronation. It is important to treat over-pronation for pain relief but also to prevent other foot conditions from developing such as Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Metatarsalgia, Post-Tib Tendonitis and/or Bunions.
Edema in the feet can be minimized by elevating your feet as often as possible and selecting footwear with a larger toe box area to allow for proper circulation. Getting your feet measured several times throughout your pregnancy is important because your foot size may change. Seamless socks and leg stretching can help promote circulation. Regular exercise, eating a well-balanced diet, avoiding foods high in salt and staying hydrated will help the body retain less fluid.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Diabetes
Definition
Diabetes is a serious disease that can develop from lack of insulin production in the body or due to the inability of the body’s insulin to perform its normal everyday functions. Insulin is a substance produced by the pancreas gland that helps process the food we eat and turn it into energy. Diabetes affects approximately 38 million Americans and is classified into 2 different types: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 is usually associated with juvenile diabetes and is often linked to heredity. Type 2, commonly referred to as adult onset diabetes, is characterized by elevated blood sugars, often in people who are overweight or have not attended to their diet properly. Many complications can be associated with diabetes. Diabetes disrupts the vascular system, affecting many areas of the body such as the eyes, kidneys, legs, and feet. People with diabetes should always pay special attention to their feet.
NEUROPATHY
Of the sixteen million Americans with diabetes, 25% will develop foot problems related to the disease. Diabetic foot conditions develop from a combination of causes including poor circulation and neuropathy. Diabetic Neuropathy can cause insensitivity or a loss of ability to feel pain, heat, and cold. People with diabetes suffering from neuropathy can develop minor cuts, scrapes, blisters, or pressure sores that they may not be aware of due to the insensitivity. If these minor injuries are left untreated, complications may result and lead to ulceration and possibly even amputation. Neuropathy can also cause deformities such as Bunions, Hammer Toes, and Charcot Feet. It is very important for people with diabetes to take the necessary precautions to prevent all foot related injuries. Due to the consequences of neuropathy, daily observation of the feet is critical. With the necessary preventative footcare measures, serious risks can be reduced.
POOR CIRCULATION
Diabetes often leads to peripheral vascular disease that inhibits a person’s blood circulation. With this condition, there is a narrowing of the arteries that frequently leads to significantly decreased circulation in the lower part of the legs and the feet. Poor circulation contributes to diabetes related foot problems by reducing the amount of oxygen and nutrition supplied to the skin and other tissue, causing injuries to heal poorly. Poor circulation can also lead to swelling and dryness of the foot. Preventing foot complications is more critical for the patient with diabetes because poor circulation impairs the healing process and can lead to ulcers, infection, and other serious foot conditions.
Treatment and Prevention
Footwear and orthotics play an important role in diabetic footcare. Orthotics designed with Plastazote foam are usually recommended. Plastazote is a material designed to accommodate pressure “hot spots” by conforming to heat and pressure. By customizing to the foot, Plastazote provides the comfort and protection needed in diabetic footcare. Footwear for those with diabetes related risks should provide the following protective benefits:
- High, wide toe box (high and wide space in the toe area)
- Removable insoles for fitting flexibility and the option to insert protective orthotics.
- Rocker Soles designed to reduce pressure in the areas of the foot most susceptible to pain, most notably the ball-of-the-foot.
- Firm Heel Counters for support and stability.
If you have diabetes, you should be particularly alert to any problems you may be having with your feet. It is very important for those with neuropathy to take necessary precautions to prevent injury and keep their feet healthy.
If you have diabetes and are experiencing a foot problem, immediately consult your foot doctor.
Overpronation
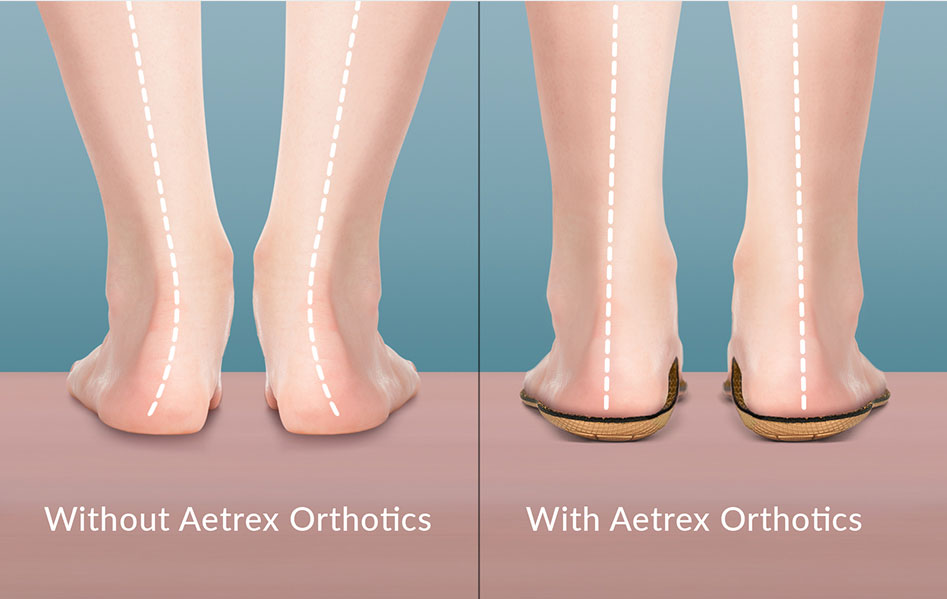
Definition
Overpronation, or flat feet, is a common biomechanical problem that occurs in the walking process when a person’s arch collapses upon weight bearing. This motion can cause extreme stress or inflammation on the plantar fascia, potentially causing discomfort and leading to other foot problems.
Cause
Overpronation is very prominent in people who have flexible, flat feet. The framework of the foot begins to collapse, causing the foot to flatten and adding stress to other parts of the foot. As a result, overpronation can lead to Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Metatarsalgia, Post-tib Tendonitis and/or Bunions.
There are many causes of flat feet. Obesity, pregnancy, or repetitive pounding on a hard surface can weaken the arch leading to overpronation. Often people with flat feet do not experience discomfort immediately, and some never suffer from any discomfort at all. However, when symptoms develop and become painful, walking becomes awkward and can cause increased strain on the feet or calves.
Treatment and Prevention
Overpronation can be treated conservatively with orthotics designed with proper arch support and medial rearfoot posting to help prevent the overpronation. Footwear should also be examined to ensure a proper fit. Footwear with firm heel counters are often recommended for extra support and stability. Improperly fitting footwear can also lead to additional foot problems.
If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.